Can You Have Intercourse After a Pap Smear?

Allo Health is dedicated to personalized well-being, offering support and trusted information tailored to individual health goals. The platform emphasizes human-generated content, led by a distinguished medical team of experts, including physicians and sexual health specialists. Their commitment to credibility involves rigorous fact-checking, authoritative research, and continuous updates to ensure accurate, up-to-date information. Allo Health's unique approach goes beyond conventional platforms, providing expert-led insights and a continuous commitment to excellence, with user feedback playing a crucial role in shaping the platform's authoritative voice.

Dr Sanina Mansoor holds MBBS degree from Yenepoya university,Mangalore.She has 8 years of experience working as a medical officer at various health centres and medical colleges.
Why This Was Upated?
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information became available.
Updated on 08 July, 2024
- Article was updated as part of our commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion.

"The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only.
Book consultation
The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog."
A pap smear is a routine gynecological procedure that checks for any abnormal cells in the cervix. It is also known as a cervical screening test. Many women wonder whether it is safe to have intercourse after a pap smear and how long they should wait before engaging in sexual activity. In this article, we will answer all your questions related to this topic and provide detailed information on the purpose of a pap smear, how to understand the results, and factors that determine when you can have intercourse after the test.
What Is a Pap Smear?
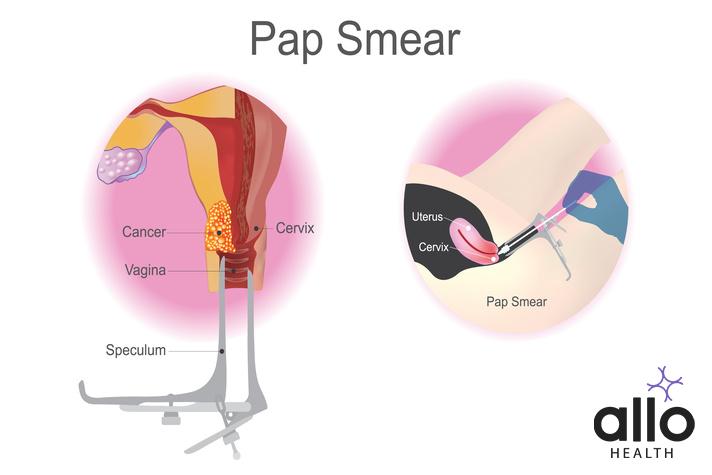
A Pap smear, also known as Pap test or cervical cytology, is a screening procedure used to detect abnormal changes in the cells of the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. The test is named after its developer, Dr. George Papanicolaou.
Here is a detailed explanation of the Pap smear procedure:
- Purpose:
- The primary purpose of a Pap smear is to identify early signs of cervical cancer or pre-cancerous conditions.
- It is not a diagnostic test for cancer but serves as a preventive measure to detect abnormalities early, allowing for timely intervention and treatment.
- When to Get a Pap Smear: Guidelines for Pap smear frequency may vary, but generally, it is recommended for women starting in their 20s or 30s, and the frequency may decrease as women age or if they have had a recent normal result.
- Procedure:
- A Pap smear is usually performed during a pelvic examination, which may include a bimanual examination of the uterus and ovaries.
- The healthcare provider uses a speculum to open the vaginal canal, providing a clear view of the cervix.
- A small brush or spatula is used to gently collect cells from the cervix. This process is quick and may cause mild discomfort but should not be painful.
- Cell Collection: The collected cells are then transferred onto a glass slide or placed in a liquid medium (liquid-based cytology) for laboratory analysis.
- Laboratory Analysis:
- The cells are examined under a microscope by a cytotechnologist or pathologist.
- The goal is to identify any abnormal changes in the cells, such as precancerous or cancerous cells.
- Results:
- Results are reported as either normal, abnormal, or inconclusive.
- Abnormal results may indicate the presence of atypical cells or other abnormalities that may require further investigation.
- Follow-up:
- Depending on the results, further diagnostic tests or treatments may be recommended.
- If abnormalities are detected early, interventions such as colposcopy, biopsy, or excisional procedures can be performed to prevent the progression to cervical cancer.
- HPV Testing: In some cases, a Pap smear may be combined with human papillomavirus (HPV) testing, as persistent infection with high-risk HPV types is a major risk factor for cervical cancer.
Regular Pap smears have played a crucial role in reducing the incidence and mortality of cervical cancer by enabling the early detection and treatment of precancerous lesions. It is essential for women to discuss with their healthcare providers the appropriate screening schedule based on their age, medical history, and risk factors.
Pap Smear Indications
Pap smears are recommended as a part of routine gynecological care for the screening and early detection of cervical cancer and its precursors. The indications for Pap smears include:
- Age and Sexual Activity: Pap smears are typically initiated for most women between the ages of 21 and 29. It is generally recommended to start screening at age 21 or within three years of becoming sexually active, whichever comes first.
- Frequency of Screening: The frequency of Pap smears can vary based on age, health history, and risk factors. Generally, it is recommended every three years for women aged 21-29. For women aged 30-65, screening every three years with Pap smear alone or every five years with Pap smear combined with HPV testing may be recommended.
- HPV Co-Testing: Human papillomavirus (HPV) co-testing, where both Pap smear and HPV test are performed together, is often recommended for women aged 30 and older. HPV is a major risk factor for cervical cancer, and detecting high-risk HPV types along with Pap smear results can enhance the accuracy of screening.
- Post-Hysterectomy: Women who have had a total hysterectomy (removal of the uterus and cervix) for non-cancerous reasons may not need Pap smears. But, if the hysterectomy was performed due to cervical cancer or precancerous conditions, Pap smears may still be necessary.
- Immunocompromised Individuals: Women with weakened immune systems, such as those living with HIV or undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, may be at an increased risk of developing cervical abnormalities. In such cases, healthcare providers may recommend more frequent Pap smears.
- Abnormal Pap Smear History: Women who have had abnormal Pap smear results in the past may require more frequent screenings or additional diagnostic tests to monitor and manage any persistent abnormalities.
- History of Cervical Dysplasia or Cancer: Women with a history of cervical dysplasia or cervical cancer may need more frequent Pap smears or other follow-up tests to monitor for recurrence or new developments.
- History of DES Exposure: Women whose mothers took the drug diethylstilbestrol (DES) during pregnancy may have an increased risk of developing cervical cancer. These individuals may need more frequent Pap smears.
- Vaccination Status: While the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine does not eliminate the need for Pap smears, it can reduce the risk of cervical cancer. The vaccination status may be considered in determining the screening frequency.
Women should discuss their individual health history, risk factors, and lifestyle with their healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate screening schedule for Pap smears and other preventive measures. Regular gynecological check-ups are crucial for overall reproductive health and early detection of any abnormalities.
Can You Have Intercourse After a Pap Smear?
After a Pap smear, it is generally advisable to avoid sexual intercourse for a short period to allow the cervix to recover. Here are some details regarding this:
- Immediate Post-Pap Smear Period:
- It’s common for healthcare providers to recommend refraining from sexual intercourse for at least 24 to 48 hours after a Pap smear.
- The reason for this recommendation is to allow the cervix to recover from the sampling procedure. The cells on the cervix may be slightly irritated or more prone to bleeding during this time.
- Possible Discomfort: Engaging in sexual activity too soon after a Pap smear may cause discomfort or slight bleeding, as the cervix may still be sensitive.
- Communication with Healthcare Provider: If you have any concerns or questions about post-Pap smear activities, it’s important to communicate with your healthcare provider. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific situation.
- Individual Variations: The recommended waiting period can vary among healthcare providers, and individual circumstances may also influence the advice given. Some providers may suggest waiting longer, while others may indicate that it’s safe to resume sexual activity sooner.
- Other Activities: In addition to refraining from sexual intercourse, it’s generally advisable to avoid using tampons, douches, or engaging in strenuous physical activities immediately after a Pap smear to minimize the risk of irritation or bleeding.
- Follow Healthcare Provider’s Guidance: Always follow the guidance provided by your healthcare provider. They may give you specific instructions based on their assessment of your situation, and you should adhere to their recommendations for your own well-being.
It’s essential to note that while there may be a recommended waiting period for sexual activity after a Pap smear, the procedure itself is generally well-tolerated, and any discomfort or spotting is usually minimal. If you experience prolonged or severe pain, heavy bleeding, or other concerning symptoms after a Pap smear, it’s crucial to contact your healthcare provider promptly for further guidance and evaluation.
Most Asked Questions
-
Can I have intercourse immediately after a Pap smear?
It is generally advisable to wait at least 24 to 48 hours after a Pap smear before engaging in sexual intercourse. This allows the cervix to recover from the sampling procedure and minimizes the risk of discomfort or bleeding.
-
What happens if I have sex too soon after a Pap smear?
Having intercourse too soon after a Pap smear may cause discomfort, spotting, or slight bleeding. The cervix may still be sensitive, and refraining from sexual activity for the recommended time helps prevent irritation.
-
Is it safe to use tampons after a Pap smear?
It is generally recommended to avoid using tampons immediately after a Pap smear. Using pads instead can help minimize any potential irritation or disruption to the cervix during the initial recovery period.
-
Can I engage in strenuous physical activities right after a Pap smear?
Strenuous physical activities, such as heavy lifting or intense exercise, are best avoided immediately after a Pap smear. Giving the cervix time to recover can reduce the risk of discomfort, bleeding, or other potential concerns.
-
What should I do if I experience pain or heavy bleeding after sex post-Pap smear?
If you encounter prolonged pain, heavy bleeding, or other concerning symptoms after sexual activity following a Pap smear, it's crucial to contact your healthcare provider promptly. They can provide guidance, assess your situation, and address any potential complications or concerns.










































