Why Do Men Need to Urinate After Ejaculation?

Allo Health is dedicated to personalized well-being, offering support and trusted information tailored to individual health goals. The platform emphasizes human-generated content, led by a distinguished medical team of experts, including physicians and sexual health specialists. Their commitment to credibility involves rigorous fact-checking, authoritative research, and continuous updates to ensure accurate, up-to-date information. Allo Health's unique approach goes beyond conventional platforms, providing expert-led insights and a continuous commitment to excellence, with user feedback playing a crucial role in shaping the platform's authoritative voice.

Welcome to my profile! I’m Dr Simran Shamanur, a dedicated and compassionate certified Sexologist with over 5 years of learning and experience in this field. I have treated over 1000 patients by helping them lead healthier, happier and more fulfilling lives by addressing their sexual health concerns. My approach is one of empathy, confidentiality and the right treatment for sexual concerns. I understand that discussing sexual health concerns can be sensitive and challenging. I provide a safe, non-judgemental and confidential environment where you can openly express your concerns and questions. Together, we will work to find personalised solutions to your specific needs.
Why This Was Upated?
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information became available.
Updated on 24 July, 2024
- Article was updated as part of our commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion.
"The following blog article provides general information and insights on various topics. However, it is important to note that the information presented is not intended as professional advice in any specific field or area. The content of this blog is for general educational and informational purposes only.
Book consultation
The content should not be interpreted as endorsement, recommendation, or guarantee of any product, service, or information mentioned. Readers are solely responsible for the decisions and actions they take based on the information provided in this blog. It is essential to exercise individual judgment, critical thinking, and personal responsibility when applying or implementing any information or suggestions discussed in the blog."
If you’re a man, you’ve probably noticed that you feel the urge to urinate immediately after ejaculation. This phenomenon is so common that it’s almost taken for granted. But have you ever wondered why this happens?
Ejaculation and Urination: The Physiology
Ejaculation and urination might seem like unrelated bodily functions, but they’re actually closely intertwined. The urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body, also plays a crucial role in ejaculation.
During sexual arousal, the two sphincter muscles at the base of the bladder begin to contract in preparation for ejaculation. This pushes any urine remaining in the urethra back into the bladder, in order to prevent it from being expelled during ejaculation.
Once ejaculation occurs, the muscles in the urethra and bladder relax, allowing semen to be expelled from the body. At this point, any urine that was pushed back into the bladder during arousal is now released, leading to the sudden urge to urinate.
Interestingly, the muscles involved in ejaculation and urination are controlled by different parts of the nervous system:
Ejaculation is controlled by the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the body’s fight or flight response.
On the other hand, urination is controlled by the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the body’s rest and digest response.
This is why it’s possible for men to experience both ejaculation and urination at the same time, despite the fact that they’re controlled by different parts of the nervous system.
In some cases, concerns with ejaculation or urination can be a sign of an underlying medical condition. For example, erectile dysfunction can be a symptom of cardiovascular disease, while difficulty urinating can be a sign of an enlarged prostate.
If you’re experiencing any concerns with either of these bodily functions, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
The Male Reproductive System: Understanding the Basics
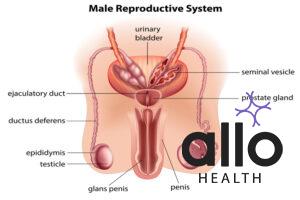
In order to fully understand why men need to urinate after ejaculation, it’s important to have a basic knowledge of the male reproductive system. The male reproductive system is comprised of several organs, including the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, prostate gland, seminal vesicles, and urethra.
The testes are responsible for producing sperm, which are stored in the epididymis until ejaculation.
The vas deferens is the tube that carries sperm from the epididymis to the prostate gland, where it mixes with seminal fluid to form semen.
The prostate gland and seminal vesicles are responsible for producing the seminal fluid that nourishes and protects sperm during ejaculation.
Finally, the urethra is the tube that carries semen and urine out of the body.
One important function of the male reproductive system is the production of testosterone, which is responsible for the development of male characteristics such as facial hair, deep voice, and muscle mass. Testosterone is produced in the testes and is regulated by the pituitary gland in the brain.
Another important aspect of the male reproductive system is the process of spermatogenesis, which is the production of mature sperm cells. This process takes place in the seminiferous tubules of the testes and involves several stages of cell division and differentiation.
What Happens to the Bladder During Ejaculation?
During sexual arousal, the bladder begins to fill up with urine. This is because the brain sends a signal to the bladder, telling it to relax and allow urine to flow into it. As a result, urine accumulates in the bladder until the body is ready to expel it.
Once the body begins to prepare for ejaculation, the muscles at the base of the bladder begin to contract. This causes the bladder to empty its contents back into the body, in order to prevent urine from mixing with semen during ejaculation.
Not all individuals experience this bladder contraction during ejaculation. Some may still have urine present in the bladder during ejaculation, which can lead to a condition known as retrograde ejaculation. This occurs when semen is redirected into the bladder instead of being expelled through the penis. Retrograde ejaculation is not harmful, but it can affect fertility in some cases.
Post-Ejaculatory Urinary Symptoms: What to Expect
After ejaculation, most men experience a sudden urge to urinate. This is because the muscles that were responsible for preventing urine from mixing with semen during ejaculation have now relaxed, allowing urine to flow freely once again.
In addition to the urge to urinate, some men may also experience symptoms such as:
- Discomfort or pain while urinating
- A weak urine stream
- Or sensation of incomplete bladder emptying.
These symptoms are usually temporary and should resolve on their own within a few hours or days.
However, if these symptoms persist or worsen over time, it may be a sign of an underlying medical condition such as a urinary tract infection or prostate concern. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience prolonged or severe post-ejaculatory urinary symptoms.
Is It Normal to Urinate After Ejaculation?
Yes, it is perfectly normal for men to need to urinate after ejaculation. In fact, it’s so common that it’s considered a normal part of the male sexual response cycle.
While some men may find this sudden urge to urinate to be inconvenient or uncomfortable, it’s important to remember that it’s a natural bodily function. There’s no need to worry or feel embarrassed about it.
One reason why men may feel the need to urinate after ejaculation is due to the fact that the urethra, which is the tube that carries urine and semen out of the body, is shared by both functions. This means that when semen is released during ejaculation, it can also stimulate the urge to urinate.
It’s also worth noting that urinating after sex can help to prevent urinary tract infections (UTIs) in both men and women. This is because it helps to flush out any bacteria that may have entered the urethra during sexual activity.
The Benefits of Urinating After Sex
In addition to preventing urine from mixing with semen during ejaculation, there are several other benefits to urinating after sex.
- Help to prevent urinary tract infections (UTIs)
During sex, bacteria from the genital area can enter the urethra and cause an infection in the urinary tract. By urinating after sexual intercourse, men can help to flush out any bacteria that may have entered the urethra, reducing their risk of developing a UTI.
- Help reduce the risk of developing bladder infections
When bacteria enter the bladder, they can cause an infection that can be painful and uncomfortable. By urinating after sex, men can help to flush out any bacteria that may have entered the bladder, reducing their risk of developing a bladder infection.
Preventing Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) in Men:

While UTIs are more common in women, men can still develop them. In addition to urinating after sex, there are several other steps men can take to reduce their risk of developing a UTI:
- Drink plenty of water to flush out the urinary tract.
- Practice good hygiene, especially around the genital area.
- Avoid holding in urine for long periods of time.
- Empty the bladder completely when urinating, in order to prevent urine from remaining in the bladder.
- Avoid using spermicides or other irritants in the genital area.
Certain medical conditions, such as an enlarged prostate or kidney stones, can increase a man’s risk of developing a UTI. Men with these conditions should work closely with their healthcare provider to manage their condition and reduce their risk of developing a UTI.
In some cases, antibiotics may be necessary to treat a UTI in men. Failure to complete the full course of antibiotics can lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
The Connection Between Prostate Health and Post-Ejaculatory Urination
The prostate gland plays a crucial role in male sexual and reproductive health. It produces the fluid that makes up a significant portion of semen, and also helps to propel semen out of the body during ejaculation & adds volume to the semen.
In some cases, concerns with the prostate gland can lead to post-ejaculatory urination concerns. For example, an enlarged prostate gland can put pressure on the urethra, making it more difficult to urinate. This can cause symptoms such as difficulty starting urination, weak stream of urine, and the need to strain in order to urinate.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a healthcare provider. They can help to determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Post-ejaculatory urination concerns can also be a symptom of other conditions, such as urinary tract infections or sexually transmitted infections. It’s important to discuss any symptoms with a healthcare provider to rule out any underlying health concerns.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Post-Ejaculatory Urination Concerns
While post-ejaculatory urination is typically a normal bodily function, there are some cases where it may be a sign of an underlying health issue. If you’re experiencing any of the following symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention:
- Frequent urination
- Pain or discomfort while urinating
- Blood in the urine
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
- Incontinence (loss of bladder control)
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, don’t hesitate to make an appointment with your healthcare provider. They can help to determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Final Words:
While the sudden urge to urinate after ejaculation may be inconvenient or uncomfortable, it’s a natural part of the male sexual response cycle. By understanding the science behind ejaculation and urination and practicing good hygiene and urinary habits, men can help to protect their reproductive and urinary health.
Post-ejaculatory urination concerns can also occur in women. While less common, women may experience discomfort or pain during or after sexual activity, as well as urinary symptoms such as frequent urination or incontinence. If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the symptoms of urinary tract infection?
A: Common symptoms of urinary tract infection (UTI) include frequent and urgent need to urinate, burning or pain during urination, and cloudy urine or bloody urine. Other signs may include strong or foul-smelling urine, lower abdominal pain or discomfort. If you suspect a UTI, seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Q: What are treatment options for frequent urge to urinate after ejaculation?
A: Treatment recommendations for frequent urge to urinate after ejaculation may include antibiotics if a urinary tract infection (UTI) is present, lifestyle changes like avoiding irritants and caffeine, and pelvic floor exercises to improve bladder control. Consulting a healthcare professional is essential to determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment.
Q: Can frequent urination after ejaculation be a sign of a medical condition?
A: In some cases, frequent urination after ejaculation could be a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as prostatitis or urinary tract issues. If this symptom is persistent or concerning, medical evaluation is advisable.
Q: Can lifestyle changes help with frequent urination after ejaculation?
A: Yes, lifestyle changes such as reducing caffeine intake, staying hydrated, maintaining good genital hygiene, and practicing pelvic floor exercises can potentially help improve bladder control and reduce frequent urination after ejaculation.











































